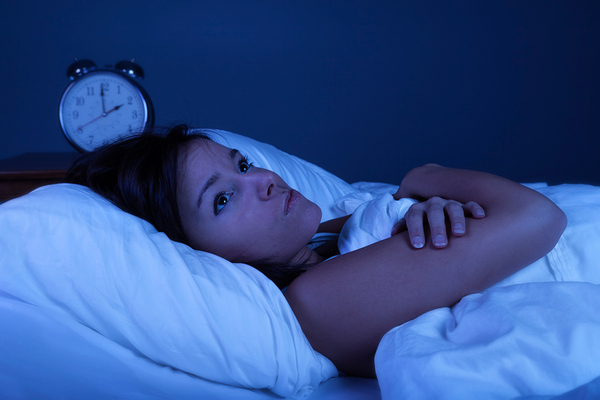
Common Reasons for Difficulty Falling Asleep
- Stress and Anxiety
- Explanation: Stress and anxiety are among the most common culprits for sleep difficulties. When your mind is racing with worries about work, relationships, or other life concerns, it becomes challenging to relax and fall asleep.
- Solution: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation before bed. Creating a calming bedtime routine can also signal to your body that it’s time to unwind.
- Poor Sleep Environment
- Explanation: Your sleep environment plays a significant role in your ability to fall asleep. Factors such as noise, light, and room temperature can disrupt your sleep.
- Solution: Make your bedroom a sleep-friendly environment. Keep the room cool, dark, and quiet. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to block out disturbances.
- Irregular Sleep Schedule
- Explanation: Inconsistent sleep patterns can disrupt your body’s internal clock, making it difficult to fall asleep. Irregular sleep schedules often arise from shift work, frequent travel, or inconsistent bedtimes.
- Solution: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your circadian rhythm, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally.
- Diet and Caffeine Consumption
- Explanation: What you eat and drink, especially close to bedtime, can significantly impact your sleep. Caffeine and heavy, spicy, or sugary foods can interfere with your ability to fall asleep.
- Solution: Limit caffeine intake, particularly in the afternoon and evening. Opt for a light, balanced dinner, and avoid large meals or snacks just before bed.
- Lack of Physical Activity
- Explanation: Regular physical activity promotes better sleep, but a sedentary lifestyle can lead to sleep difficulties.
- Solution: Incorporate at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise into your daily routine. However, avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it can be stimulating and make it harder to fall asleep.
- Exposure to Blue Light
- Explanation: Blue light from screens (phones, tablets, computers, TVs) inhibits melatonin production, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep.
- Solution: Reduce screen time at least an hour before bed. Use blue light filters on your devices or switch to red or warm light settings in the evening.
- Medical Conditions
- Explanation: Certain medical conditions, such as insomnia, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and chronic pain, can make it difficult to fall asleep.
- Solution: If you suspect a medical condition is affecting your sleep, consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.
- Mental Health Issues
- Explanation: Conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, and PTSD can lead to sleep problems. Negative thought patterns and emotional distress can prevent you from relaxing and falling asleep.
- Solution: Seek professional help from a therapist or counselor to address underlying mental health issues. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia can be particularly effective.
Practical Tips to Improve Sleep
1. Establish a Bedtime Routine
Creating a consistent and relaxing pre-sleep routine can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This might include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing gentle yoga or meditation.
2. Limit Naps
While short naps can be beneficial, long or irregular napping during the day can interfere with nighttime sleep. If you need to nap, try to keep it to 20-30 minutes and avoid napping late in the afternoon or evening.
3. Mind Your Sleep Hygiene
Good sleep hygiene involves habits that promote regular, restful sleep. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and electronics before bed.
4. Manage Stress and Anxiety
Finding effective ways to manage stress can help you relax and fall asleep more easily. Consider techniques such as journaling, talking to a friend or therapist, or engaging in hobbies that help you unwind.
5. Use Sleep Aids Sparingly
While over-the-counter sleep aids can be helpful for occasional sleeplessness, they are not a long-term solution. Relying on sleep aids can lead to dependency and may not address the underlying issues causing your sleep difficulties.
6. Practice Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation can help quiet a racing mind and promote relaxation. Apps and guided meditation sessions can provide structured ways to incorporate these practices into your routine.
7. Consider Sleep Supplements
Natural supplements such as melatonin, valerian root, and magnesium can support sleep. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you’ve tried various strategies and still struggle with falling asleep or staying asleep, it may be time to seek professional help. Persistent sleep issues can indicate underlying conditions such as insomnia, sleep apnea, or other sleep disorders. Consulting a healthcare provider or a sleep specialist can provide a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.